Beauty Secrets, Did You Know?
What Is Glycation & How Does It Affect Your Skin?
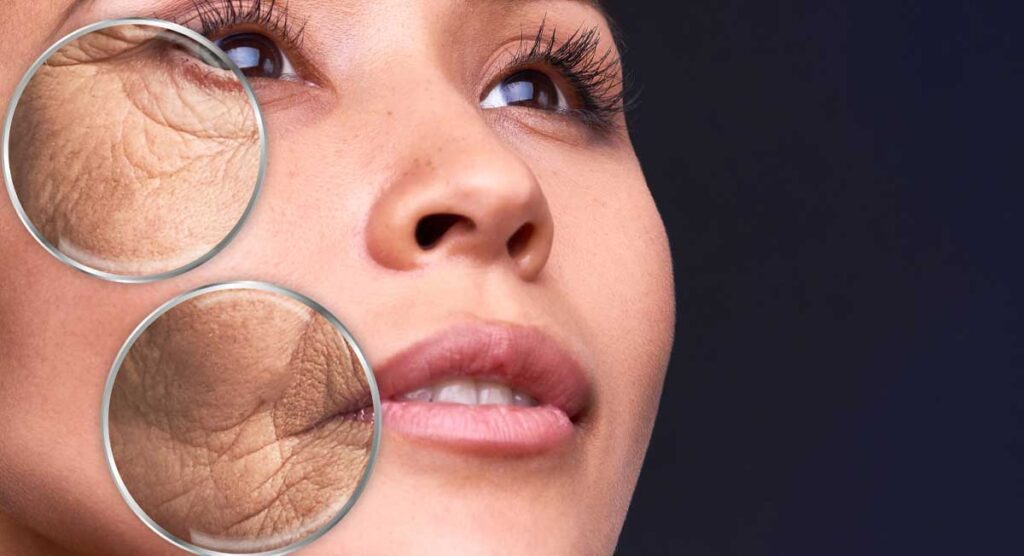
You probably know that sugar, stress, and UV exposure can harm your skin. But did you know that these three factors have something in common? All of these external factors cause a natural process in the body called glycation, which is linked to many specific skin problems. Learn more about the glycation process, how it affects your skin, and what you can do to reverse and prevent its effects.
What is glycation?
Glycation is a natural chemical reaction that causes sugar molecules like glucose or fructose to bind to proteins and lipids throughout the body, including the skin. The result is the formation of advanced glycation end products. When this happens, the proteins and lipids involved in the glycation process are damaged and are therefore unable to perform their normal functions properly.
When sugar molecules bind to collagen and elastin proteins in the skin, for example, these important proteins are unable to properly support the structure of the skin, leading to wrinkles and other signs of accelerated aging.
So what triggers this reaction? Several factors can cause glycation, including high sugar intake, increased blood glucose levels due to stress, and oxidative stress caused by UV exposure, air pollution, or poor lifestyle habits.
Skin problems caused by glycation
Glycation can affect the skin in many different ways. Here are some of the main problems it causes:
Fine lines and wrinkles:
- When collagen and elastin proteins are damaged by the glycation process, fine lines, wrinkles, and areas of loose or sagging skin become visible on the surface of the skin. These proteins are essential components of healthy, youthful skin.
Compromised barrier function. The skin’s protective barrier consists of a bilayer of lipids. When these lipids are damaged by glycation, the barrier is unable to properly perform its two primary functions:
- to retain moisture
- to keep out harmful allergens and irritants.
The result of poor skin barrier function is, therefore, dehydration and irritation.
Inflammation:
- Glycation has also been shown to activate inflammatory pathways throughout the body, worsening inflammatory skin conditions such as acne, eczema, and rosacea.
Can glycation be reversed?
While it is impossible to stop glycation completely, it is possible to slow it down and reverse its effects, or even prevent it in the future. Our bodies can use antioxidants to fight the negative effects of glycation, but this defense is often insufficient in the face of accelerated glycation.
The first step in reducing glycation and its effects on the skin is to avoid or significantly reduce exposure to the factors that cause it: sugar consumption, UV radiation, chronic stress, etc.
Combine this step with the right skin care products for your particular skin type and concerns. Anti-aging ingredients such as heparan sulfate, defensins, and retinoids can help reduce wrinkles and other signs of skin aging.
A skin barrier repair moisturizer such as B-Box Kalm Emulsion or Renewable Moisturizer can restore the natural lipid balance within the skin barrier, restoring its moisturizing and protective function to the skin.
Anti-inflammatory skin care ingredients such as Argan Oil, Green Tea, Allantoin, Feverfew, Aloe Vera, and many others help deactivate inflammatory pathways, reducing redness, itching, and irritation. You will find aloe vera gel in almost all B-Box Bio products.
Conclusion
Some glycation occurs naturally in the body, but high levels caused by excessive glycation can wreak havoc on the body and skin. Combine a healthy lifestyle with a skincare regimen tailored to your skin type and needs to combat these effects and achieve the healthy, beautiful skin you want.


 Français
Français